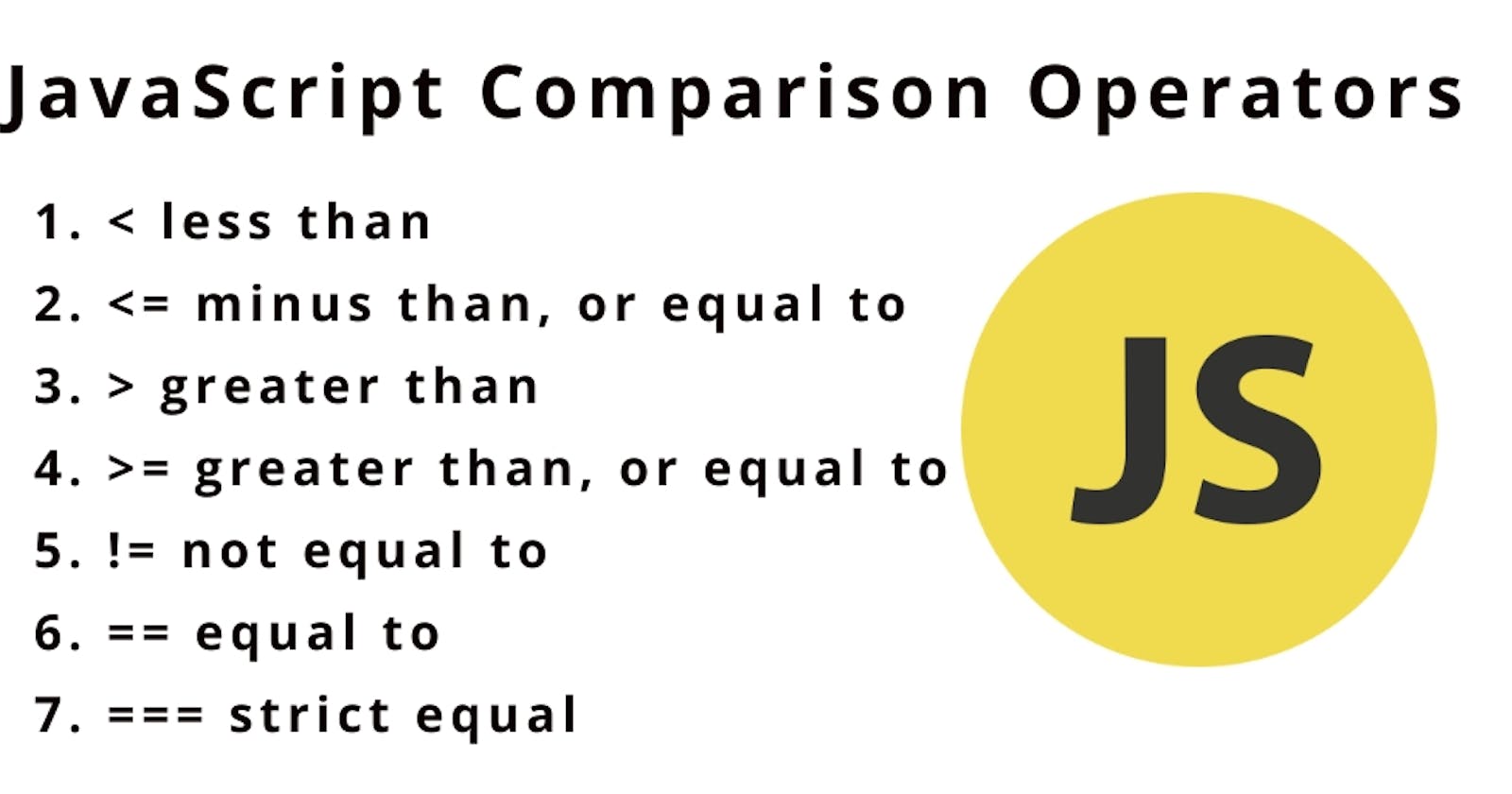
Comparison operators are used in comparing operands and return a boolean value (true or false). In JavaScript, comparison operators except for the strict equality and inequality operators, convert operands to a common data type when comparing. This is called Type Coercion.
Comparison Operators in Javascript
Equality Operator (==)
a == bwould returntrueif the value of a is equal to the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Example
3 == 3; //true
3 == '3'; //true (type coercion)
1 == 2; //false
Strict Equality Operator (===)
Unlike the equality operator, the strict equality operator compares values as-is without converting the data types.
3 === '3'would returnfalsebecause 3 is a number and '3' is a string while3 === 3would returntruebecause they are the same data type.Inequality Operator (!=)
a != bwould returntrueif the value of a is not equal to the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Example
1 != 2; //true
1 != '1'; //false (type coercion makes 1 = '1')
1 != true; //false (1 = true)
0 != false; //false (0 = false)
Strict Inequality Operator (!==)
Whereas1 != trueand1 != '1'would returnfalse,1 !== trueand1 !== '1'would returntruebecause the operands are of different data types. This is because Strict Inequality Operator does not convert data types when comparing.
Examples
3 !== 3; //false
3 !== '3'; //true
4 !== 3; //true
Greater-than Operator (>)
a > bwould returntrueif the value of a is greater than the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Examples
5 > 3; //true
'1' > 2; //false (type coercion)
1 > 2; //false
Greater-than-or-equal-to Operator (>=)
a >= bwould returntrueif the value of a is greater than or equal to the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Examples
6 >= 3; //true
'10' >= 10; //true (type coercion)
1 >= 2; //false
Less-than Operator (<)
a < bwould returntrueif the value of a is less than the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Examples
5 < 3; //false
'1' < 2; //true (type coercion)
1 < 2 ;//true
Less-than-or-equal-to Operator (<=)
a <= bwould returntrueif the value of a is less than or equal to the value of b. Otherwise, it would returnfalse.
Examples
6 <= 3; //false
'10' <= 10; //true (type coercion)
1 <= 2; //true
Logical And Operator (&&)
num > a && num <= bwould returntrueif both statements are true. Otherwise, It would returnfalse.
Examples
2 > 3 && 2 < 1; //false
2 == '2' && 2 <3; //true
1 <= 3 && 5 > 6; //false
Logical Or Operator (||)
num > a || num <= bwould returntrueif either statements is true. Otherwise, It would returnfalse.
Examples
2 > 3 && 2 < 1; //false
2 == '2' && 2 < 3; //true
1 <= 3 && 5 > 6; //true
Check out the sites below for more information on Comparison in JavaScript